Generating Nerve Impulses
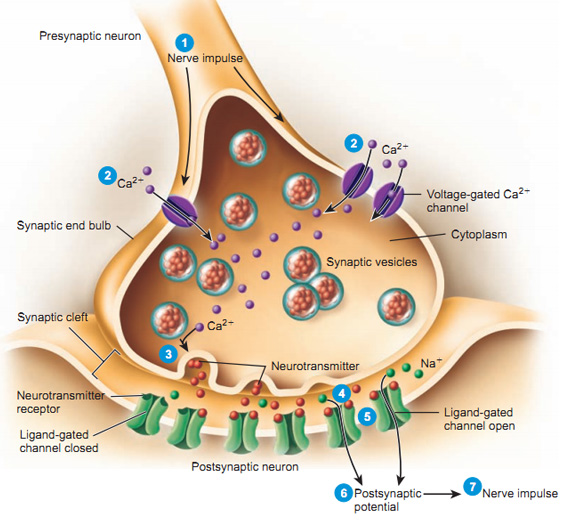
Nerve Impulse Transmission Within a Neuron To do 9 min read 4 min video All functions performed by the nervous system—from a simple motor reflex to more advanced functions like making a memory or a decision—require neurons to communicate with one another. You're signed out. Videos you watch may be added to the TV's watch history and influence TV recommendations. To avoid this, cancel and sign in to YouTube on your computer. Nerve impulses have a domino effect. Each neuron receives an impulse and must pass it on to the next neuron and make sure the correct impulse continues on its path. Through a chain of chemical events, the dendrites (part of a neuron) pick up an impulse that’s shuttled through the axon and transmitted to the. Nerve impulses are traveling electrochemical signals that change in charge as they travel along a nerve channel. The transmission of electrical energy along a nerve is typically measured in millivolts (+30mV to ‑70 mV), with times measured in milliseconds. Speeds range from 10 to 100 meters per second. Transmission of nerve impulse across a synapse by chemical means was discovered in 1936 by Sir Henry Hallet Dale, a British Pharmacologist and Nobel laureate, 1875-1968. It occurs as under- i) When an impulse arrives at the synaptic knob of the axon, it depolarizes the presynaptic membrane and increases its permeability to calcium ions (Ca+).
A nerve impulse, like a lightning strike, is an electrical phenomenon. A nerve impulse occurs because of a difference in electrical charge across the plasma membrane of a neuron. How does this difference in electrical charge come about? The answer involves ions, which are electrically charged atoms or molecules.
Resting Potential
When a neuron is not actively transmitting a nerve impulse, it is in a resting state, ready to transmit a nerve impulse. During the resting state, the sodium-potassium pump maintains a difference in charge across the cell membrane of the neuron. The sodium-potassium pump is a mechanism of active transport that moves sodium ions out of cells and potassium ions into cells. The sodium-potassium pump moves both ions from areas of lower to higher concentration, using energy in ATP and carrier proteins in the cell membrane. Figure (PageIndex{3})shows in greater detail how the sodium-potassium pump works. Sodium is the principal ion in the fluid outside of cells, and potassium is the principal ion in the fluid inside of cells. These differences in concentration create an electrical gradient across the cell membrane, called resting potential. Tightly controlling membrane resting potential is critical for the transmission of nerve impulses.
The human nervous system is the body’s regulation and communication centre. It can be divided into two parts: the central nervous system which comprises the encephalon (brain, diencephalon, cerebellum and brain stem) and the spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system formed by the nerves attached to the central nervous system.
The nervous system receives information about changes in the body and then decides to act on this information if necessary. One part of the nervous system is called voluntary, as it concerns nervous impulses transmitted to the muscles which we can control consciously. The other part is named involuntary as it concerns the nervous impulses on which we have no influence, like the heartbeat or digestion for example. Nervous impulses thus ensure message transmission within the body.
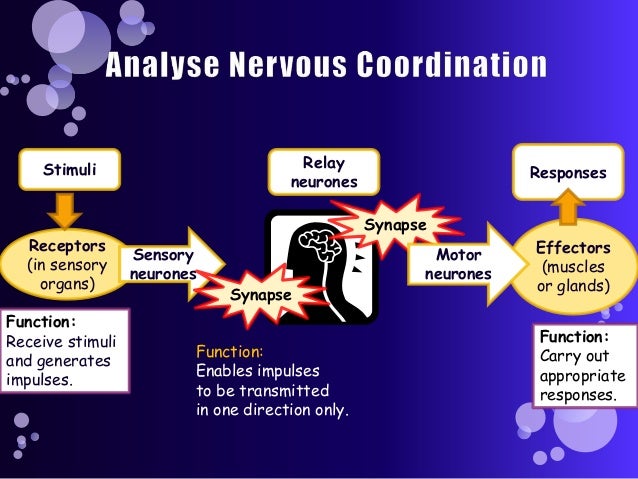
The nervous impulse is also called ‘action potential’. It refers to the electric signal produced by a neuron when stimulated. This signal is then transmitted by synapses, or connections between the cells. There are two types of nervous impulses. The first pass from the skin’s receptors or from internal organs to the brain and relay information from the brain to the muscles and glands. The others transmit information between two types of neurons.
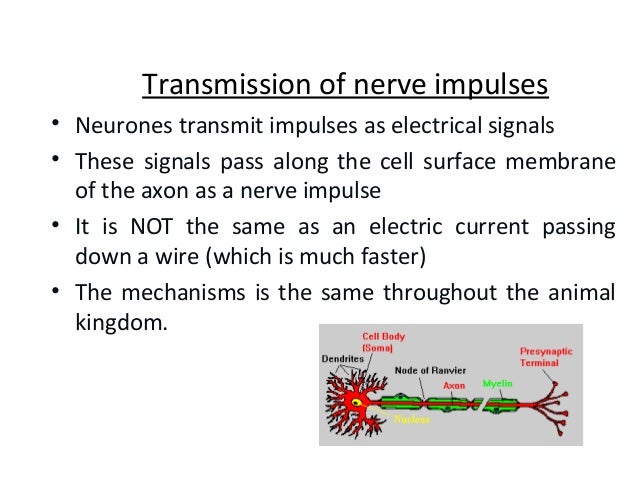
While an electric current circulates at a speed of around 300 000 km per second, nervous impulses in the human body are much slower: 100 m per second. This speed is still more than enough to transmit information extremely quickly through the body.
Neurophysiology Of Nerve Impulses

Livre
How Are Nerve Impulses Transmitted Within A Neuron
MARIEB, Elaine N., 2005. Anatomie et physiologie humaines. Adaptation de la 6ème édition américaine (René Lachaîne). Pearson Education France.
